
This is also sometimes called an ellipsoidal joint.

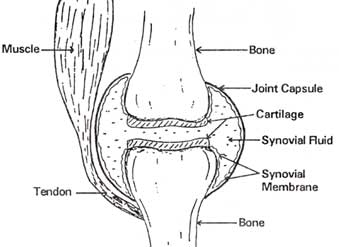
The fluid lubricates the joint, reducing friction between the bones and allowing for greater movement. This space is referred to as the joint cavity and is filled with fluid. Synovial joints are the only joints that have a space between the adjoining bones. Cartilaginous joints allow for very little movement. An example is found at the joints between vertebrae, the so-called “disks” of the backbone. The joints between the bones in the skull and between the teeth and the bone of their sockets are examples of fibrous joints.Ĭartilaginous joints are joints in which the bones are connected by cartilage. There is no cavity, or space, present between the bones, so most fibrous joints do not move at all, or are only capable of minor movements. The bones of fibrous joints are held together by fibrous connective tissue. The structural classification divides joints into fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial joints depending on the material composing the joint and the presence or absence of a cavity in the joint.

There are two ways to classify joints: based on their structure or based on their function. Joints are responsible for movement, such as the movement of limbs, and stability, such as the stability found in the bones of the skull. The point at which two or more bones meet is called a j oint, or articulation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
